Chapter 6, Reproduction in Animals, explains the processes of reproduction in detail, including both sexual and asexual methods. It covers fertilization, embryo development, and internal and external fertilization differences. Designed for Class 8 students, this chapter helps them understand the basics of animal reproduction with simple explanations and examples, making it ideal for study and exam preparation.
1) What are the two modes of reproduction in animals?
Answer: The two modes of reproduction in animals are asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
2) What is asexual reproduction?
Answer: Asexual reproduction is the process by which a single organism produces genetically identical offspring.
3) What are some examples of animals that reproduce asexually?
Answer: Some examples of animals that reproduce asexually include:
Hydra
Starfish
Planarian
4) What is sexual reproduction?
Answer: Sexual reproduction is the process by which two organisms combine their genetic material to produce offspring that are genetically different from both parents.
5) What are the male and female reproductive organs in humans?
Answer: The male reproductive organs in humans include the testes, scrotum, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and urethra. The female reproductive organs in humans include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and cervix.
6) What is fertilization?
Answer: Fertilization is the process by which a sperm cell unites with an egg cell to form a zygote.
7) What is the difference between internal and external fertilization?
Answer: Internal fertilization occurs when the sperm cell fertilizes the egg cell inside the female's body. External fertilization occurs when the sperm cell fertilizes the egg cell outside the female's body.
8) What is the role of hormones in reproduction?
Answer: Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate the reproductive system. They control the development of reproductive organs, the production of sperm and eggs, and the menstrual cycle in females.
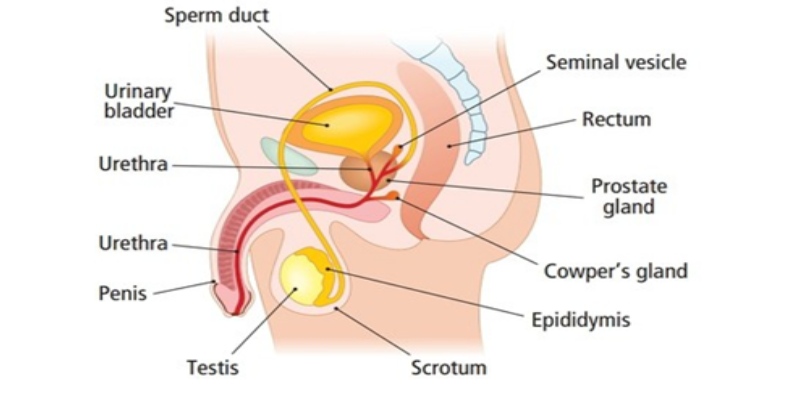
9) What are the main components of the male reproductive system?
Answer: The main components of the male reproductive system are the testes, sperm ducts, and the penis.
10) What is the function of the testes?
Answer: The testes produce male gametes called sperms.
11) What are the parts of a sperm?
Answer: A sperm has a head, a middle piece, and a tail.
12) How many sperm are produced by the testes?
Answer: Millions of sperm are produced by the testes.
13) What are the main components of the female reproductive system?
Answer: The main components of the female reproductive system are the ovaries, oviducts, and the uterus.
14) What is the function of the ovaries?
Answer: The ovaries produce female gametes called ova.
15) What is the role of the oviducts?
Answer: The oviducts carry the ova from the ovaries to the uterus.
16) What is the function of the uterus?
Answer: The uterus is a muscular organ where a fertilized ovum can implant and develop into a fetus.
17) What is the first step in the process of reproduction?
Answer: The first step in the process of reproduction is the fusion of a sperm and an ovum.
18) What happens during fertilization?
Answer: During fertilization, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus.
19) What is the result of fertilization?
Answer: The result of fertilization is the formation of a fertilized egg or zygote.
20) What type of fertilization occurs in humans, cows, dogs, and hens?
Answer: Internal fertilization occurs in humans, cows, dogs, and hens.
21) In what type of animals does fertilization take place outside the body?
Answer: Fertilization takes place outside the body in aquatic animals such as fish, starfish, etc.
22) Dolly is the healthy identical twin of Finn Dorsett sheep or Scottish blackface ewe?
Answer: Finn Dorsett sheep.
23) How does fertilization occur in aquatic animals like fish, starfish, etc. animals?
Answer: In these animals, the male deposits sperm over the eggs in water. The sperm swim randomly and come in contact with the eggs. This results in the fusion of the sperm and the egg, which is called external fertilization.
24) Why do fish and frogs lay hundreds of eggs, while a hen lays only one egg at a time?
Answer: The number of eggs laid by an animal depends on factors such as egg size, survival chances of offspring, and parental care. Fish and frogs lay many small eggs with low survival chances and provide no parental care. Hens lay fewer, larger eggs with higher survival chances and provide parental care.
25) What is the result of fertilization?
Answer: Fertilization results in the formation of a zygote.
26) What happens to the zygote after it is formed?
Answer: The zygote begins to divide repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells.
27) What are the developing groups of cells called?
Answer: The developing groups of cells are called tissues and organs.
28) What is the developing structure called?
Answer: The developing structure is called an embryo.
29) Where does the embryo get embedded for further development?
Answer: The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus.
30) How does the embryo continue to develop?
Answer: The embryo continues to develop in the uterus and gradually forms body parts.
31) What happens to the embryo after it forms body parts?
Answer: The embryo continues to develop in the uterus and forms body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, and ears.
32) What is the stage of the embryo called when all body parts can be identified?
Answer: The stage of the embryo is called a fetus.
33) What happens when the development of the fetus is complete?
Answer: When the development of the fetus is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
34) What are the two types of animals based on how they give birth to their offspring?
Answer: The two types are viviparous and oviparous animals.
35) What are viviparous animals?
Answer: Viviparous animals are those that give birth to young ones.
36) What are oviparous animals?
Answer: Oviparous animals are those that lay eggs.
37) What are examples of viviparous animals?
Answer: Examples of viviparous animals include humans, cows, dogs, and hens.
38) What are examples of oviparous animals?
Answer: Examples of oviparous animals include frogs, lizards, butterflies, moths, hens, and crows.
39) What happens to newborn individuals that are born or hatched from eggs?
Answer: They continue to grow until they become adults.
40) In some animals, how do the young ones look compared to the adults?
Answer: In some animals, the young ones may look very different from the adults.
41) What are the different stages in the life cycle of a frog?
Answer: The three stages are egg, tadpole (larva), and adult.
42) How do tadpoles look compared to adults?
Answer: Tadpoles look very different from adults.
43) What are the drastic changes that occur in tadpoles?
Answer: The drastic changes are called metamorphosis.
44) Do human beings also undergo metamorphosis?
Answer: No, human beings do not undergo metamorphosis. Body parts similar to those present in adults are present from birth.
45) What is budding?
Answer: Budding is a type of asexual reproduction where new individuals develop as outgrowths from a single parent.
46) In what organism does budding occur?
Answer: Budding occurs in hydra.
47) What is the first step in asexual reproduction in amoeba?
Answer: The first step is the division of the nucleus into two nuclei.
48) What happens after the nucleus divides in amoeba?
Answer: The body divides into two parts, with each part receiving a nucleus.
49) What is the type of asexual reproduction in amoeba called?
Answer: The type of asexual reproduction in amoeba is called binary fission.
50) What is binary fission?
Answer: When an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals this is called binary fission.
51) What is cloning?
Answer: Cloning is the production of the exact copy of a cell, any other living part, or a complete organism.
52) Who performed the first successful cloning?
Answer: Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland.
53) What is the name of the successfully cloned sheep?
Answer: Dolly.